Getting Started with Camunda 8
In this article, the set-up of the Adapter is explained step by step. Additionally, you can try out some of the functionalities of the Adapter following the instructions in this article.
What you'll need
- An IDE of your choice (IntelliJ recommended)
- Java 17
- Maven
- Camunda Modeler Version >= 5.40.0
- Postgres or Docker (to set up postgres database)
- Postman or any similar tool for creating API requests
- Working KADAI application (e.g. see our Spring-Boot-Example here)
Note: Please name your packages, folders and files exactly like in the example!
Step 0 (optional): Download and start C8 run
If you don't have a Camunda 8 application that you could use for experimenting with the Adapter,
install a new application. You can use C8 run for
this. Download a version >= 8.8.0 of C8
run.
Use this guide
to start C8 run. Make sure to use
the shutdown script
when stopping C8 run. You can check whether C8 run is running properly by logging in to
http://localhost:8081/operate with username and password demo.
Step 1: Initialize an empty Adapter application
You can skip steps 1-3 if you want to use our example Adapter application. You can find it in our GitHub repository.
Use
this Spring Initializr-Configuration
to create an example Maven Project.
It is already configured to our needs, you can simply click GENERATE.
Unpack the project and open it in an IDE of your choice. Your project-structure should look like below:
demo
├───.mvn
│ └───wrapper
├───src
│ ├───main
│ └───test
│ .gitignore
│ HELP.md
│ mvnw
│ mvnw.cmd
│ pom.xml
Step 2: Configure your Adapter application
Add the following dependencies to the dependencies section of your pom (if they don't already exist):
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.kadai</groupId>
<artifactId>kadai-adapter</artifactId>
<version>11.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.kadai</groupId>
<artifactId>kadai-adapter-camunda-8-system-connector</artifactId>
<version>11.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.kadai</groupId>
<artifactId>kadai-adapter-kadai-connector</artifactId>
<version>11.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Add the following annotations to your AdapterApplication, and import the packages correspondingly:
@EnableScheduling
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "io.kadai.adapter")
@Import({AdapterConfiguration.class})
Add the following files to your resources folder:
application.properties
######################################################################################
## Adapter properties
######################################################################################
##
logging.level.io.kadai=WARN
## Set Server Port for Adapter
server.port=18082
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true
kadai.adapter.run-as.user=taskadmin
kadai.adapter.scheduler.run.interval.for.start.kadai.tasks.in.milliseconds=10000
kadai.adapter.scheduler.run.interval.for.complete.referenced.tasks.in.milliseconds=10000
kadai.adapter.scheduler.run.interval.for.claim.referenced.tasks.in.milliseconds=10000
kadai.adapter.scheduler.run.interval.for.cancel.claim.referenced.tasks.in.milliseconds=10000
kadai.adapter.scheduler.run.interval.for.check.finished.referenced.tasks.in.milliseconds=10000
####################################################################################
# Kadai-connector properties
####################################################################################
#
# Configure the datasource for Kadai DB (used by kadai-connector)
kadai.adapter.events.lockDuration=300
kadai.adapter.sync.kadai.batchSize=1
kadai.datasource.jdbcUrl=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5102/postgres
kadai.datasource.driverClassName=org.postgresql.Driver
kadai.datasource.username=postgres
kadai.datasource.password=postgres
kadai.schemaName=kadai
kadai.adapter.mapping.default.objectreference.company=DEFAULT_COMPANY
kadai.adapter.mapping.default.objectreference.system=DEFAULT_SYSTEM
kadai.adapter.mapping.default.objectreference.system.instance=DEFAULT_SYSTEM_INSTANCE
kadai.adapter.mapping.default.objectreference.type=DEFAULT_TYPE
kadai.adapter.mapping.default.objectreference.value=DEFAULT_VALUE
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
management.health.external-services.enabled=true
####################################################################################
# Camunda 8 properties
####################################################################################
camunda.client.mode=self-managed
camunda.client.enabled=true
camunda.client.rest-address=http://localhost:8081
# avoid warning logs if a job worker does not fetch jobs frequently enough
logging.level.io.camunda.client.job.poller=ERROR
# temporary fix bad-scoped for health-beans: these are just dummy values!
kadai-system-connector-camundaSystemURLs=http://localhost:8081|http://localhost:8081
Step 3: Add SPIs to your Adapter application
SPIs need to be additionally specified in the Adapter application. You can read more about
SPIs here.
The necessary SPI for the Adapter application can be built as follows: First, create a new package
with the name taskrouting.
Then, create a class in the package taskrouting with the name ExampleTaskRouter. It should look
like this:
package com.example.demo.taskrouting; //or your own path depending on your packages
import io.kadai.common.api.KadaiEngine;
import io.kadai.spi.routing.api.TaskRoutingProvider;
import io.kadai.task.api.models.Task;
/** This is a sample implementation of TaskRouter. */
public class ExampleTaskRouter implements TaskRoutingProvider {
@Override
public void initialize(KadaiEngine kadaiEngine) {
// no-op
}
@Override
public String determineWorkbasketId(Task task) {
return "WBI:100000000000000000000000000000000001";
}
}
Next, add a new folder to your resources folder and name it META-INF.
Create a new folder named services inside of the folder META-INF.
Finally, in the services folder, create a file named
io.kadai.spi.routing.api.TaskRoutingProvider.
This file must contain the fully qualified classname (including the package) of the class
ExampleTaskRouter, for example:
com.example.demo.taskrouting.ExampleTaskRouter
Make sure there aren't any empty lines in this file. The finished structure of the source folder should look like this:
demo
├───.mvn
├───src
│ ├───main
│ │ ├───java
│ │ │ └───com
│ │ │ └───example
│ │ │ └───adapter
│ │ │ │───taskrouting
│ │ │ │ ExampleTaskRouter.java
│ │ │ │───AdapterApplication.java
│ │ └───resources
│ │ │───META-INF.services
│ │ io.kadai.spi.routing.api.TaskRoutingProvider
│ │ │───application.properties
│ │ │───kadai.properties
│ ...
│ pom.xml
Step 4: Start all applications together
Then, start your KADAI application together with Postgres. Make sure to use the same version as specified in the pom.xml of your adapter. Start your camunda app next, and login. Last, start the adapter.
Step 5: Try out different functionalities of Adapter
-
Start a process with a User Task in Camunda. You can use this example process:
Or find it in our GitHub repository. Open the diagram in the Camunda Modeler and click on "file deployment" (Rocket sign in the lower left corner). Here, you can connect to your Camunda 8 instance by entering
http://localhost:26500as the Cluster endpoint: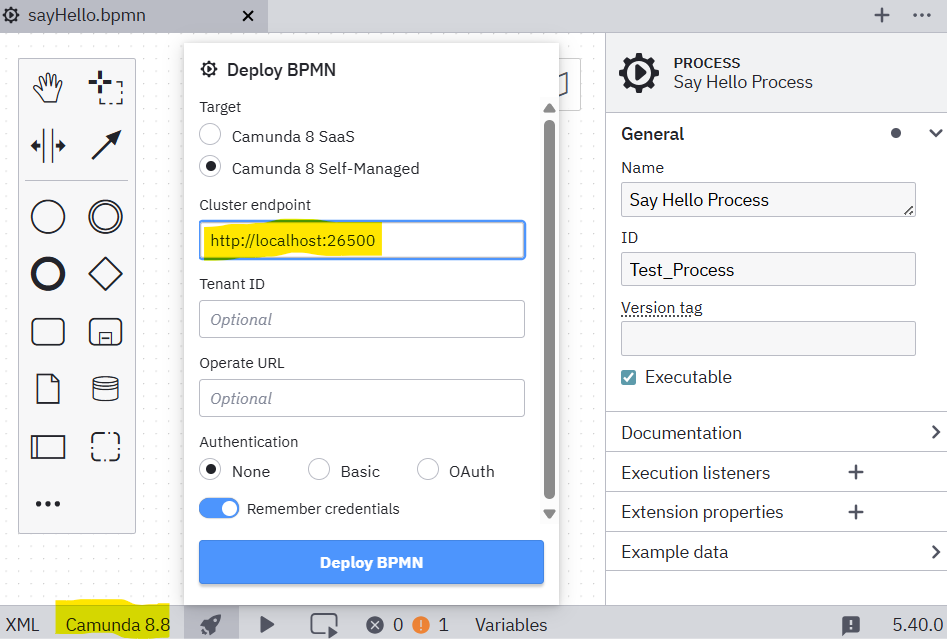
After connecting, you can deploy the process by clicking on "Deploy BPMN". Next, start a new instance by clicking on "Open start instance" (Play sign in the lower left corner) and then "Start BPMN process instance":
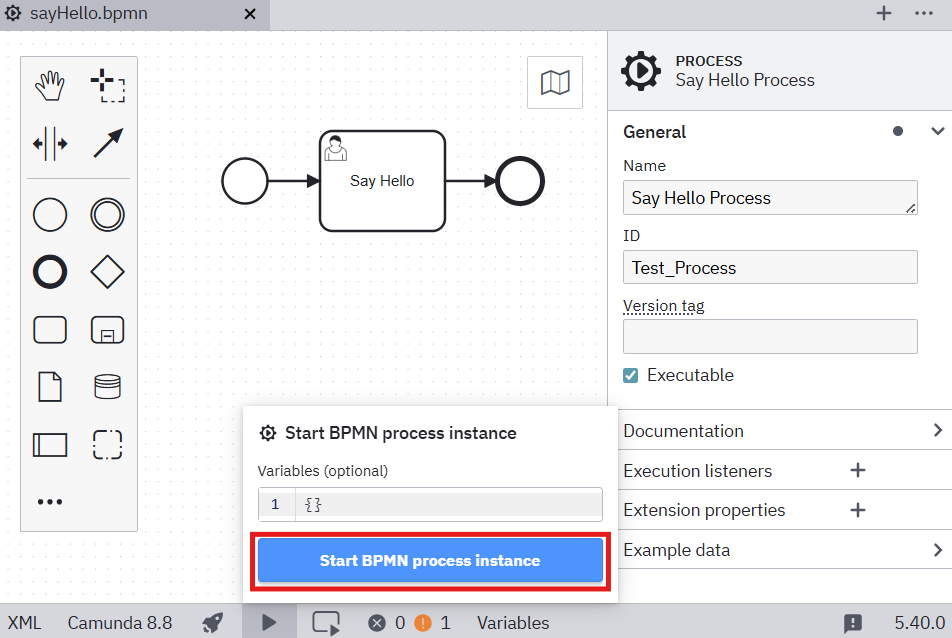
-
The User Task should be imported to KADAI automatically. You can check it by first knowing the name of the user task from the started process, then make a postgres GET request to KADAI using the following request, entering the name (or just substring of the name) of the user task for the "name-like" attribute.
GET http://localhost:8080/kadai/api/v1/tasks?name-like=Say helloMake sure that the correct port number is used for KADAI request. You can check the port number in
application.propertiesof KADAI underserver.port. If not specified, then the default port is8080. You have to authenticate yourself using Basic Auth: In Postman, go to the "Authorization" tab. There, selectbasicAuthand typeadminas user andadminas password. Make sureenableCsrfis set to false in theapplication.propertiesof the KADAI application.The response to the request should look like this:
{
"tasks": [
{
"taskId": "TKI:f807830a-44e2-4c50-9f35-43dd945e2b31",
"externalId": "c8sysid-0-utk-2251799813691243",
"created": "2025-10-24T09:50:59.867Z",
"claimed": null,
"completed": null,
"modified": "2025-10-24T09:50:59.867Z",
"planned": "2025-12-02T11:00:00Z",
"received": null,
"due": "2025-12-22T10:59:59.999Z",
"name": "Say Hello Task",
"creator": "taskadmin"
}
, ...
],
...
} -
Claim the KADAI Task from the previous step using Postman. Make sure you add the following property to the
application.propertiesfile of the adapter application:kadai.adapter.camunda.claiming.enabled=true, then restart the adapter. To send the POST request, use the same authorization as in the previous step. The Task should get claimed in Camunda automatically.POST http://localhost:8080/kadai/api/v1/tasks/{taskid}/claimYou can check that the task in KADAI is also claimed by making the same GET Request as in Step 1 and see the
claimedattribute. -
Complete the KADAI Task from the previous step using Postman. To send the POST request, use the same authorization as in the previous step. The Task should disappear from Camunda Tasklist.
POST http://localhost:8080/kadai/api/v1/tasks/{taskid}/completeNow check in Camunda Operate that the task is completed.
More functionalities like the cancelling of a claimed task and their URLs can be found in the full documentation of the REST-API.